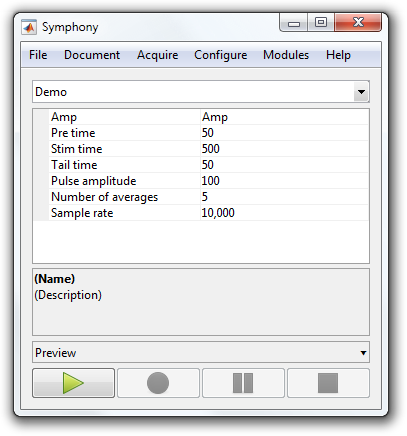
Write a Protocol
This tutorial shows how to write a Protocol.
- Step 1: Create a class
- Step 2: Add properties
- Step 3: Override prepareEpoch
- Step 4: Override shouldContinuePreparingEpochs
- Step 5: Override shouldContinueRun
Step 1: Create a class
A Protocol is simply a MATLAB class that subclasses from symphonyui.core.Protocol.
Create a new class in your personal Symphony package by navigating to the package in MATLAB's Current Folder, right-clicking on the "+protocols" directory, and selecting New File > Class.
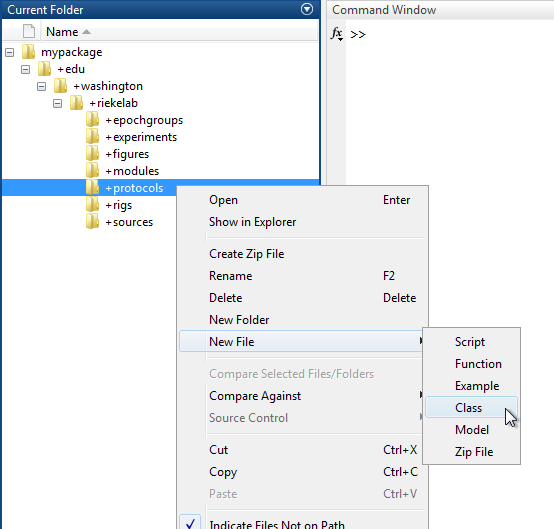
Name the class file "Demo.m" and open it in the MATLAB Editor.
classdef Demo
%DEMO Summary of this class goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
properties
end
methods
end
end
Remove the comments and edit the classdef line to subclass from the symphonyui.core.Protocol class.
classdef Demo < symphonyui.core.Protocol
properties
end
methods
end
end
You now have an empty Protocol.
Step 2: Add properties
The properties of a Protocol define the user-configurable values that populate the Protocol Properties section of the main window when your protocol is selected.
Add a few properties to the "Demo" properties block to accept user-configurable values for a pulse.
classdef Demo < symphonyui.core.Protocol
properties
amp
preTime
stimTime
tailTime
pulseAmplitude
numberOfAverages
end
methods
end
end
Add a default value and comment to each property to make the protocol more user-friendly.
classdef Demo < symphonyui.core.Protocol
properties
amp = 'Amp' % Output amplifier
preTime = 50 % Pulse leading duration (ms)
stimTime = 500 % Pulse duration (ms)
tailTime = 50 % Pulse trailing duration (ms)
pulseAmplitude = 100 % Pulse amplitude (mV)
numberOfAverages = 5 % Number of epochs
end
methods
end
end
You now have a Protocol with user-configurable properties.
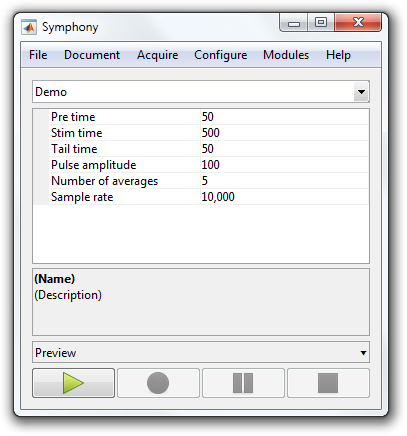
| Note: All protocols inherit a "sampleRate" property. |
Step 3: Override prepareEpoch
The behavior of a protocol is defined by overriding methods of the symphonyui.core.Protocol superclass. The methods include (not a complete list):
prepareRun(obj)- Override to perform actions before the start of the first epoch.prepareEpoch(obj, epoch)- Override to perform actions before each epoch is added to the epoch queue.completeEpoch(obj, epoch)- Override to perform actions after each epoch is completed.shouldContinuePreparingEpochs(obj)- Override to return true/false to indicate if this protocol should continue preparing epochs.shouldContinueRun(obj)- Override to return true/false to indicate if this protocol should continue run.completeRun(obj)- Override to perform actions after the last epoch has completed.
Override the prepareEpoch() method in the "Demo" protocol so you can add a stimulus and response to each epoch.
classdef Demo < symphonyui.core.Protocol
properties
amp = 'Amp' % Output amplifier
preTime = 50 % Pulse leading duration (ms)
stimTime = 500 % Pulse duration (ms)
tailTime = 50 % Pulse trailing duration (ms)
pulseAmplitude = 100 % Pulse amplitude (mV)
numberOfAverages = 5 % Number of epochs
end
methods
function prepareEpoch(obj, epoch)
end
end
end
Whenever you override a Protocol method you always want to call the superclass first so it can perform default behavior. Add a call to the superclass method in the "Demo" prepareEpoch() method.
function prepareEpoch(obj, epoch)
[email protected](obj, epoch);
end
Add a pulse stimulus to the amplifier in each epoch by using a PulseGenerator and calling the addStimulus() method on the epoch passed to prepareEpoch().
function prepareEpoch(obj, epoch)
[email protected](obj, epoch);
gen = symphonyui.builtin.stimuli.PulseGenerator();
gen.preTime = obj.preTime;
gen.stimTime = obj.stimTime;
gen.tailTime = obj.tailTime;
gen.amplitude = obj.pulseAmplitude;
gen.mean = 0;
gen.sampleRate = obj.sampleRate;
gen.units = 'mV';
stimulus = gen.generate();
device = obj.rig.getDevice(obj.amp);
epoch.addStimulus(device, stimulus);
end
Add a response from the amplifier in each epoch by calling addResponse().
function prepareEpoch(obj, epoch)
[email protected](obj, epoch);
gen = symphonyui.builtin.stimuli.PulseGenerator();
gen.preTime = obj.preTime;
gen.stimTime = obj.stimTime;
gen.tailTime = obj.tailTime;
gen.amplitude = obj.pulseAmplitude;
gen.mean = 0;
gen.sampleRate = obj.sampleRate;
gen.units = 'mV';
stimulus = gen.generate();
device = obj.rig.getDevice(obj.amp);
epoch.addStimulus(device, stimulus);
epoch.addResponse(device);
end
You now have a Protocol that produces epochs with a pulse stimulus presented to, and a response recorded from, the amplifier device.
Step 4: Override shouldContinuePreparingEpochs
A protocol needs to indicate when it no longer wants to prepare any more epochs. This is generally done when the number of prepared epochs equals the number of epochs specified by the user through a protocol property, like numberOfAverages.
All protocols keep track of the current number of prepared epochs in a numEpochsPrepared property. Override the shouldContinuePreparingEpochs() method in "Demo" to return false when the numEpochsPrepared is greater than or equal to numberOfAverages.
function tf = shouldContinuePreparingEpochs(obj)
tf = obj.numEpochsPrepared < obj.numberOfAverages;
end
Note: shouldContinuePreparingEpochs() and shouldContinueRun() are some of the few protocol methods you can override without worrying about calling their superclass method. However there is also no harm in doing so.
|
You now have a Protocol that will prepare the number of epochs equal to the value of numberOfAverages.
Step 5: Override shouldContinueRun
A protocol also needs to indicate when it no longer wants to run. This is generally done when the number of completed epochs equals the number of epochs specified by the user.
All protocols keep track of the current number of completed epoch in a numEpochsCompleted property. Override the shouldContinueRun() method in "Demo" to return false when the numEpochsCompleted is greater than or equal to numberOfAverages.
function tf = shouldContinueRun(obj)
tf = obj.numEpochsCompleted < obj.numberOfAverages;
end
You now have a fully functioning Protocol.
classdef Demo < symphonyui.core.Protocol
properties
amp = 'Amp' % Output amplifier
preTime = 50 % Pulse leading duration (ms)
stimTime = 500 % Pulse duration (ms)
tailTime = 50 % Pulse trailing duration (ms)
pulseAmplitude = 100 % Pulse amplitude (mV)
numberOfAverages = 5 % Number of epochs
end
methods
function prepareEpoch(obj, epoch)
[email protected](obj, epoch);
gen = symphonyui.builtin.stimuli.PulseGenerator();
gen.preTime = obj.preTime;
gen.stimTime = obj.stimTime;
gen.tailTime = obj.tailTime;
gen.amplitude = obj.pulseAmplitude;
gen.mean = 0;
gen.sampleRate = obj.sampleRate;
gen.units = 'mV';
stimulus = gen.generate();
device = obj.rig.getDevice(obj.amp);
epoch.addStimulus(device, stimulus);
epoch.addResponse(device);
end
function tf = shouldContinuePreparingEpochs(obj)
tf = obj.numEpochsPrepared < obj.numberOfAverages;
end
function tf = shouldContinueRun(obj)
tf = obj.numEpochsCompleted < obj.numberOfAverages;
end
end
end
If your personal package is in the Symphony path you should now be able to run the "Demo" protocol from the main window (it will not show any figures while running, however, until you show figure handlers).